How to Become a CT Tech: A Complete Guide to Starting Your Career in Radiologic Technology
A career as a CT (computed tomography) tech can be highly rewarding, offering the chance to work in a dynamic healthcare environment and assist in diagnosing patients using advanced imaging technology. If you’re interested in pursuing this path, here’s a step-by-step guide to becoming a CT tech, including educational requirements, certifications, and tips on building a successful career.
1. Understand the Role of a CT Tech
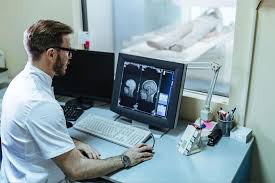
A CT tech, or CT technologist, operates CT scanners to create diagnostic images of a patient’s body. These images help doctors diagnose and monitor various medical conditions. CT techs are responsible for:
- Preparing and positioning patients for scans
- Operating CT equipment and ensuring image quality
- Following radiation safety protocols
- Assisting physicians with interpreting the images
- Communicating with patients to help them feel comfortable
CT techs work in hospitals, outpatient centers, and diagnostic imaging facilities, where they collaborate with doctors, radiologists, and other healthcare professionals.
2. Complete an Associate Degree in Radiologic Technology
The typical educational path for becoming a CT tech starts with an associate degree in radiologic technology or a related field. This degree usually takes about two years to complete and includes coursework in:
- Anatomy and physiology
- Patient care and safety
- Radiation protection and physics
- Image production and evaluation
- Radiographic procedures and equipment handling
Program Recommendations:
- Look for programs accredited by the Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology (JRCERT). This ensures that your education meets industry standards.
- Many community colleges and technical schools offer radiologic technology programs, often with clinical practice in healthcare settings to give hands-on experience.
3. Obtain State Licensing (if required)
Some states require radiologic technologists to be licensed. Licensing requirements vary, so it’s important to check with your state’s health department or medical board. This may involve passing an exam or fulfilling specific education and training requirements.
4. Earn Certification as a Registered Radiologic Technologist (RT)
Certification through the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) can improve job prospects and career advancement. To become certified:
- Pass the ARRT Radiography Examination after completing your degree.
- Maintain ARRT certification by following continuing education requirements and adhering to professional standards.
Certification as an ARRT Registered Technologist (RT) is often a prerequisite for pursuing CT-specific certification, and it shows employers that you have a solid foundation in radiology.
5. Gain Experience in Radiology
Most CT technologists begin their careers working as radiologic technologists (RTs) to gain experience. This hands-on experience is invaluable because it:
- Provides familiarity with imaging techniques, patient care, and safety protocols.
- Helps build relationships with mentors and supervisors who can guide you.
- Allows you to develop the soft skills (communication, patience, attention to detail) needed for CT-specific roles.
Many employers look for candidates with at least 1-2 years of experience in general radiography before considering them for CT positions.
6. Pursue Advanced Certification in CT Imaging
To become a certified CT tech, you can earn advanced certification through the ARRT in Computed Tomography. To qualify, you’ll need:
- ARRT certification in Radiography (or a related primary pathway)
- Documented clinical experience performing CT procedures
- Passing score on the CT certification exam
ARRT’s CT certification validates your ability to operate CT equipment, follow radiation safety protocols, and produce high-quality diagnostic images. Certification can enhance your qualifications, increase job opportunities, and may lead to higher pay.
7. Find a CT Technologist Position
Once you’re certified, it’s time to look for a position as a CT tech. Healthcare facilities and job boards such as Indeed, Monster, and Glassdoor often list CT technologist positions. Networking through professional associations like the American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT) can also connect you with job opportunities and industry contacts.
8. Consider Continuing Education and Specialization
Healthcare is constantly evolving, and technology in imaging continues to advance. Staying updated with new developments through continuing education courses can make you a valuable asset. You may also want to specialize in areas like:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
- Interventional Radiology
Advanced certifications can open up opportunities for leadership roles or teaching positions.
Final Thoughts
Becoming a CT tech requires dedication to education, certification, and continuous learning. By following these steps, you can launch a fulfilling career in the healthcare industry, where you’ll play a vital role in patient diagnosis and care.
For more information on ARRT certifications, check out the ARRT website, and for details on radiologic technologist education programs, visit JRCERT.
Share this content:






Post Comment