How Long Does It Take To Become An Ultrasound Tech?
Becoming an ultrasound technician, or diagnostic medical sonographer, typically takes 1 to 4 years, depending on the educational path you choose.
1. Associate’s Degree in Diagnostic Medical Sonography
- Duration: 2 years (full-time)
- Overview: This is the most common educational path. Associate’s degree programs cover anatomy, medical ethics, imaging techniques, and sonography specialties like obstetrics, abdominal, or vascular sonography. Programs usually include clinical training for hands-on experience.
2. Certificate Program
- Duration: 1 to 1.5 years (full-time)
- Overview: Certificate programs are shorter and are often pursued by individuals who already have healthcare experience, such as nurses or radiology technicians. These programs focus primarily on sonography and typically require fewer general education courses than an associate’s degree.
3. Bachelor’s Degree in Sonography
- Duration: 4 years (full-time)
- Overview: Some students opt for a bachelor’s degree, which offers more comprehensive education and the potential for advanced career opportunities or specialization.
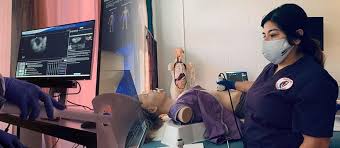
4. Clinical Training
- All educational programs require clinical training to gain hands-on experience in real healthcare settings. This is a critical part of the curriculum and typically ranges from several months to a year.
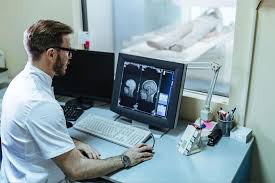
Certification and Licensing
After completing an accredited program, most states require passing a certification exam, such as the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) exam, to become licensed.
Factors Affecting Duration:
- Part-time enrollment: Can extend the program length.
- Specialization: Specializing in a specific area like vascular or cardiac sonography may require additional training.
For more details on accredited programs, visit the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP).
Share this content:





Post Comment